Madagascar is situated in between 20° 00' South latitude and 47° 00' East longitude in the Indian Ocean. The island is separated from the south eastern coast of Africa by the Mozambique Channel, of about 400 km in its narrowest point. With an area of 587,000 km², it is the fourth largest Island in the world after Greenland, New Guinea and Borneo. Madagascar was originally part of the Gondwana; it was isolated from the African continent about 140 million years ago. This has contributed to make this island so unique today, essentially because its exceptional biodiversity has evolved over time in an independent micro-continent.
History of Madagascar
The Malagasy are of mixed Malayo-Indonesian and African-Arab ancestry. Indonesians are believed to have migrated to the island about 700. King Andrianampoinimerina (1787–1810) ruled the major kingdom on the island, and his son, Radama I (1810–1828), unified much of the island. The French made the island a protectorate in 1885, and then, in 1894–1895, ended the monarchy, exiling Queen Rànavàlona III to Algiers. A colonial administration was set up, to which the Comoro Islands were attached in 1908, and other territories later. In World War II, the British occupied Madagascar, which retained ties to Vichy France.

Population of Madagascar
The singularity of the island also refers to the human history which differs in various aspects from Africa.
The current “Malagasy” population is estimated at 26 million. The country is made up of 18 different ethnic groups of different historical and geographical origins. Some historians suggest that Malagasy people have their origin from Malay and east African seafarers that arrived in the island around the first century. The earliest evidence of humans on the island dates to about 10,000 years ago. Recent research indicates that Madagascar was the refuge of European pirates and Portuguese seafarers discovered the island in 1500. The Merina and Betsileo, who reflect most the Malay features, live in the Central Highlands. East African, Arab, European and Indian traits are predominant in the coastal people that constitute the remaining ethnic groups.
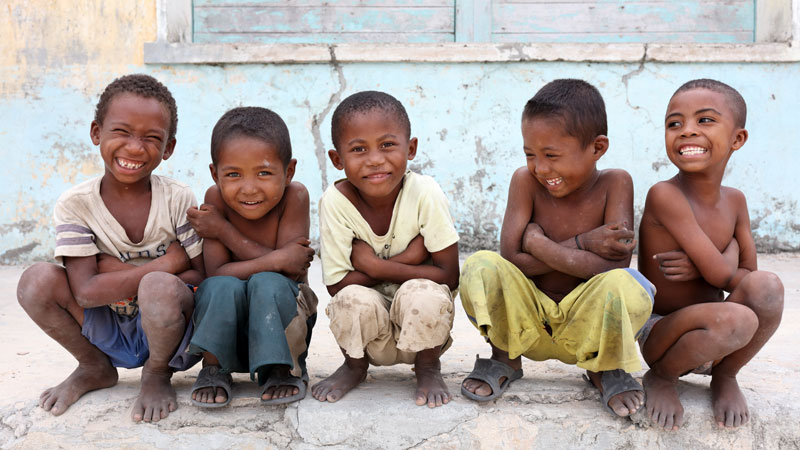

80% of the populations are living in the country side, 53% are women and 49% are children under 15. The fact is that 77% of Malagasy people are living below the international poverty line, and the country is ranked 161 out of 189 countries in theUnited Nations Human Development Report of 2018.
Culture
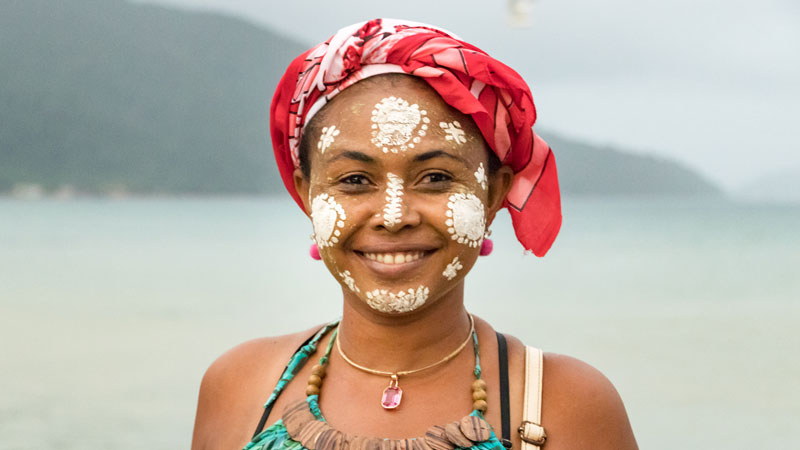

There are a number of core cultural features that are common throughout the island, creating a strongly unified Malagasy cultural identity. In addition to a common language and shared traditional religious beliefs around a creator god and veneration of the ancestors, the traditional Malagasy worldview is shaped by values that emphasize fihavanana (solidarity), vintana (destiny), tody (karma), and hasina, a sacred life force that traditional communities believe imbues and thereby legitimates authority figures within the community or family. Other cultural elements commonly found throughout the island include the practice of male circumcision; strong kinship ties; and a widespread belief in the power of magic, diviners, astrology and witch doctors.
Languages
The official languages are Malagasy and French.
Malagasy is the native language of the country, with various dialects spoken in different portions of the island. The official language is based on the Merina dialect, which is spoken in the capital of Antananarivo and the surrounding Central Highlands.
French is also widely used as a second language in education, workplace and public administration as Madagascar is a former French colony.
Climate

The climate is tropical along the coast, temperate inland, and arid in the south. Madagascar has two seasons: a hot, rainy season from November to April, and a cooler, dry season from May to October. The east coast has a sub-equatorial climate and, being most directly exposed to the trade winds, has the heaviest rainfall, averaging as much as 3500 mm annually. During the ATBC in Antananarivo, day temperatures will range from highs of about 20-22°C and lows to about 10°C, with some chance of rain, particularly in the morning.
Natural Resources
Graphite, chromite, coal, bauxite, salt, quartz, tar sands, semiprecious stones, mica, fish, hydropower.
-
Agriculture Products
Coffee, vanilla, sugarcane, cloves, cocoa, rice, cassava (tapioca), beans, bananas, peanuts; livestock products.
-
Industries
Meat processing, soap, breweries, tanneries, sugar, textiles, glassware, cement, automobile assembly plant, paper, petroleum, tourism.
-
Export Commodities
Coffee, vanilla, shellfish, sugar, cotton cloth, clothing, chromite, petroleum products.
-
Export Partners
France 15.2%, US 12.7%, China 7.1%, South Africa 5.9%, Japan 5.5%, Netherlands 5.4%, Germany 5.1%, Belgium 5%, India 4.4% (2015).
-
Import Commodities
Capital goods, petroleum, consumer goods, food.
-
Import Partners
China 24.8%, France 10.3%, Bahrain 5.6%, India 5.5%, Kuwait 4.5%, Mauritius 4.5%, South Africa 4.3% (2015).
-
Currency
Ariary and Malagasy Franc (FMG).